
What is A1C?
Does your doctor or health professional “make a big deal” about your A1C level? Wondering what the glucose to A1C amount is? Glycohemoglobin (HgbA1C or A1C) is a test designed to measure the amount of glucose bound to hemoglobin in the blood.
People who have diabetes may have more glycohemoglobin than average. Most clinical diabetes groups prefer the use of the term A1C when describing this test. A1C is useful for measuring the level of long-term glucose control. A red blood cell in the body has an average life of 3-4 months and the amount of glucose it has been exposed to during its life can be measured and reported.
This information can be used to diagnose and/or treat diabetes. If you have diabetes, your A1C level should be below 6.5%. This will reduce your chances of suffering the complications of diabetes.
What are ways to control A1C?
Monitoring your carbohydrate intake is essential to lowering blood glucose levels and therefore A1C levels. The foods you eat can have a direct impact on your blood glucose. Carbohydrate examples include potatoes, rice, bread, fruit, milk,and other starchy foods. When too many carbs are eaten, the blood sugar may rise too high. Frequent blood sugar spikes will be reflected as a high A1C level. Monitoring the intake of carbs will help lower blood sugar levels and therefore be reflected as a lower A1C level. Be careful of “hidden” sources of carbohydrate. These include breading on meat, sauces, and low fat dressings.
Label reading is important when grocery shopping. Check the total carbohydrates on the label in order to stay in your ideal carbohydrate range. Try to focus on measuring carbs and eating non-starchy vegetables, lean meats and unsaturated fats. Eating 3 medium size meals each day and 1-2 snacks will also help stabilize blood sugar. Be sure to ask your health care provider for individualized advice regarding any changes you would like to make in your eating habits. Planning ahead will increase your chances of success regarding your diet.
Exercise helps to lower your blood glucose levels by allowing your body to use its own insulin more effectively. This will, in turn, help lower HgbA1C levels. Exercise also tones and builds muscle which is more metabolically active than fat. Ask your health care professional for advice on how to start a safe exercise program.
Medications can play a very important role in lowering HgbA1C. Be sure to follow your health care provider’s advice regarding diabetes medicines. For those who are newly diagnosed with diabetes, it can be very helpful to keep a diary of foods eaten, medications taken and timing. This information can be very useful to your physician.
Some of the ways medicines can lower HgbA1C include:
cause the liver to reduce its output of glucose
adding insulin when the body is not producing a sufficient quantity
reducing insulin resistance by making the body more sensitive to it’s own insulin
cause the body to increase production of insulin
Keep in mind that illness or infection can also affect A1C. Be sure to make a note of any illnesses you may have had so you can offer your health care provider this information at your next visit.
Glucose to A1C chart:
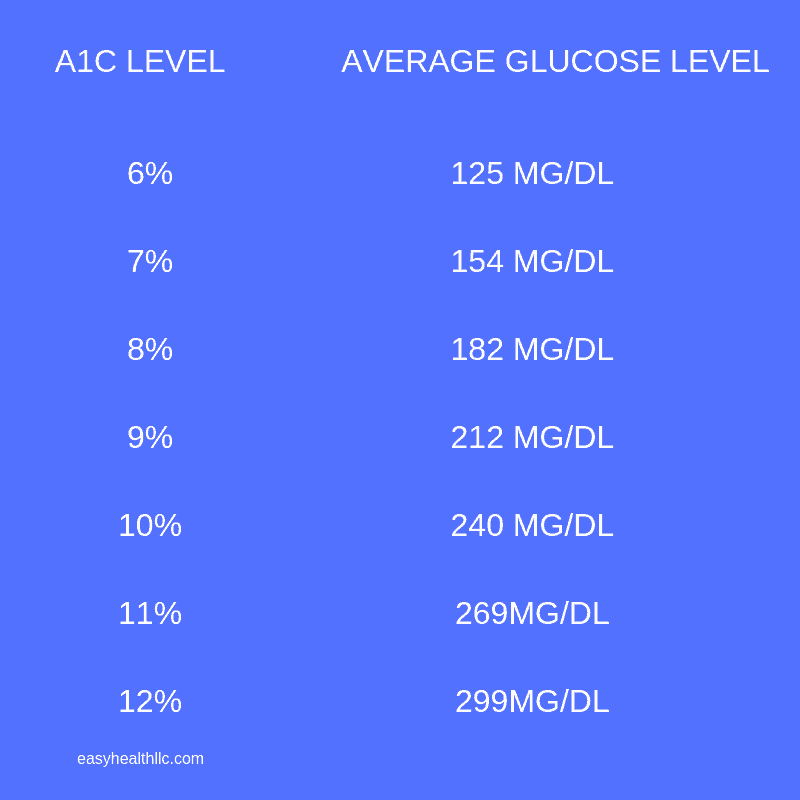
A1C Control Resources:
What is “Normal” A1C? When is it Misleading?– an article from diatribe
A1C Test and A1C Calculator – an article from Accu-Check
Health and Diabetes Resources- list of helpful resources from Easyhealth Living Blog
5 Things You Can Do Each Morning to Control Type 2 Diabetes
Share...
No comments:
Post a Comment